Because your kidneys can compensate for lost function, signs may not appear until irreversible damage has occurred.

Picture: iStock
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs on either side of your spine, below your ribs and behind your belly, roughly the size of a large fist.
The kidneys’ job is to filter or clean your blood. They remove wastes, control the body’s fluid balance, and keep the right levels of electrolytes. All of the blood in your body passes through them several times a day.
The process starts with blood coming into the kidney. Waste gets removed and salt, water, and minerals are adjusted, if needed. The filtered blood goes back into the body. Waste gets turned into urine, which collects in the kidney’s pelvis – a funnel-shaped structure that drains into a tube called the ureter to the bladder.
Each kidney has around a million tiny filters called nephrons. You could have only 10% of your kidneys working, and you may not notice any symptoms or problems. If blood stops flowing into a kidney, part or all of it could die. That can lead to kidney failure.
Chronic kidney failure is the gradual loss of kidney function described above. When chronic kidney disease reaches an advanced stage, dangerous levels of fluid, electrolytes and wastes can build up in your body.
In the early stages of chronic kidney disease, you may have few signs or symptoms.
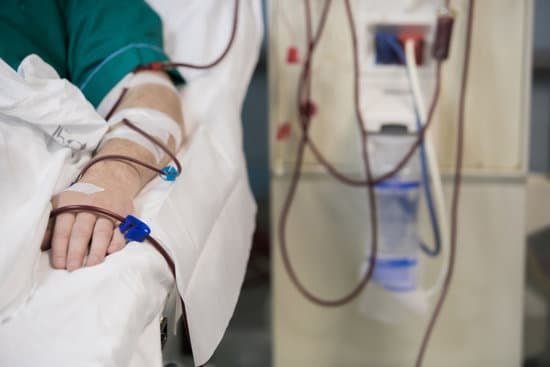
Dialysis. Picture: iStock
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease develop over time if kidney damage progresses slowly. Signs and symptoms of kidney disease may include:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Sleep problems.
- Changes in how much you urinate.
- Decreased mental sharpness.
- Muscle twitches and cramps.
- Swelling of feet and ankles.
- Persistent itching.
- Chest pain, if fluid builds up around the lining of the heart.
- Shortness of breath, if fluid builds up in the lungs.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) that’s difficult to control.

Nausea. Picture: iStock
Causes
Chronic kidney disease occurs when a disease or condition impairs kidney function, causing damage over months or years. Diseases that cause it include:
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- Glomerulonephritis, an inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units (glomeruli).
- Interstitial nephritis, an inflammation of the kidney’s tubules and surrounding structures.
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged prostate.
- Vesicoureteral reflux, a condition that causes urine to back up into your kidneys.
- Recurrent kidney infection.

Blood pressure. Picture: iStock
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk include:
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease.
- Smoking.
- Obesity.
- Family history of kidney disease.
- Abnormal kidney structure.
- Older age.
Complications
Chronic kidney disease can affect almost every part of your body. Potential complications may include:
• Fluid retention, which could lead to swelling in your arms and legs, high blood pressure, or fluid in your lungs (pulmonary oedema).
• A sudden rise in potassium levels in your blood (hyperkalaemia), which could impair your heart’s ability to function and may be life-threatening.
• Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease.
• Weak bones and an increased risk of bone fractures.
• Anaemia.
• Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction or reduced fertility.
• Damage to your central nervous system, which can cause difficulty concentrating, personality changes or seizures.
• Decreased immune response, which makes you more vulnerable to infection.
• Pericarditis, an inflammation of the saclike membrane that envelops your heart (pericardium).

Fluid retention. Picture: iStock
Prevention
To reduce your risk of developing kidney disease:
• Follow instructions on over-the-counter medications. When using nonprescription pain relievers, such as aspirin and ibrufen, follow the instructions on the package.
• Maintain a healthy weight. If you’re at a healthy weight, work to maintain it by being physically active most days of the week.
• Don’t smoke. Cigarette smoking can damage your kidneys and make existing damage worse.
• Manage your medical conditions with your doctor’s help. If you have diseases or conditions that increase your risk of kidney disease, like hypertension and diabetes, work with your doctor to control them. Ask your doctor about tests to look for signs of kidney damage.
For more news your way, download The Citizen’s app for iOS and Android.
Download our app




